Business Finance
Uni ePrep Course
Also Available at SF@NS LXP Soon

Are you an NSF, NSMan, or anyone else who wants to better prepare for university studies in Singapore or overseas? NTU’s Business Finance ePrep course is specially developed to help learners get a head start in their university studies. The course offers an excellent introduction to finance and investment, making it a must-do course for those intending to pursue degrees in business administration, finance, accountancy, and commerce. It is also highly beneficial for learners in other fields. Even those not planning to pursue further studies in the near future will find this course valuable, and it may even inspire them to consider university studies.
The Business Finance ePrep course is developed in collaboration with Cengage, the publishers of the popular textbook “Essentials of Financial Management” by Brigham and Houston. Learners are given a hard copy of this textbook at no additional cost, along with excellent eLearning materials on business finance provided by Cengage. The course also includes learning materials on economics, which complements the business finance curriculum.
The provided textbook on business financial management is used in NTU NBS and other universities in Asia. It is based on a popular American business finance textbook, with three of the chapters adapted by Asian business professors to suit the Asian environment. To further support learners, the course includes a retired NTU professor acting as a personalized tutor. Learners can reach out to him via email with any queries or questions.
It’s worth noting that this course, as well as NTU’s other ePrep courses, will soon be also available on SF@NS LXP in addition to the NS Portal and NTU PaCE’s site. There is no limit to the number of ePrep courses learners can sign up for under SF@NS LXP, making it a great opportunity to gain a competitive edge in university studies.
Business Finance ePrep Course
– Learning Contents
I. Compulsory Chapters
1. An Overview of Financial Management.
- Explain the role of finance and the different types of jobs in finance.
- Identify the advantages and disadvantages of different forms of business organization.
- Explain the links between stock price, intrinsic value, and executive compensation.
- Identify the potential conflicts that arise within the firm between stockholders and managers and between stockholders and bondholders, and discuss the techniques that firms can use to mitigate these potential conflicts.
- Discuss the importance of business ethics and the consequences of unethical behavior.
2. Financial Markets and Institutions, incorporating Singapore Stock Markets and SGX.
- Identify the different types of financial markets and financial institutions, and explain how these markets and institutions enhance capital allocation.
- Explain how the stock market operates, and list the distinctions between the different types of stock markets.
- Explain how the stock market has performed in recent years.
- Discuss the importance of market efficiency, and explain why some markets are more efficient than others.
- Develop a simple understanding of behavioral finance.
3. Financial Statements, Cash Flow, and Taxes.
- List each of the key financial statements and identify the kinds of information they provide to corporate managers and investors.
- Estimate a firm’s free cash flow and explain why free cash flow has such an important effect on firm value.
- Discuss the major features of the federal income tax system.
4. Analysis of Financial Statements.
- Explain what ratio analysis is.
- List the five groups of ratios and identify, calculate, and interpret the key ratios in each group.
- Discuss each ratio’s relationship to the balance sheet and income statement.
- Discuss why return on equity (ROE) is the key ratio under management’s control and how the other ratios impact ROE, and explain how to use the DuPont equation for improving ROE.
- Compare a firm’s ratios with those of other firms (benchmarking) and analyze a given firm’s ratios over time (trend analysis).
- Discuss the tendency of ratios to fluctuate over time (which may or may not be problematic); explain how they can be influenced by accounting practices as well as other factors; and explain why they must be used with care
5. Time Value of Money.
- Explain how the time value of money works and discuss why it is such an important concept in finance.
- Calculate the present value and future value of lump sums.
- Identify the different types of annuities, calculate the present value and future value of both an ordinary annuity and an annuity due, and calculate the relevant annuity payments.
- Calculate the present value and future value of an uneven cash flow stream. You will use this knowledge in later chapters that show how to value common stocks and corporate projects.
- Explain the difference between nominal, periodic, and effective interest rates. An understanding of these concepts is necessary when comparing rates of returns on alternative investments.
- Discuss the basics of loan amortization and develop a loan amortization schedule that you might use when considering an auto loan or home mortgage loan.
6. Financial Planning and Forecasting.
- Discuss the importance of strategic planning and the central role that financial forecasting plays in the overall planning process.
- Explain how firms forecast sales.
- Use the Additional Funds Needed (or AFN) equation and discuss the relationship between asset growth and the need for funds.
- Explain how spreadsheets are used in the forecasting process, starting with historical statements, ending with projected statements, and including a set of financial ratios based on those projected statements.
- Discuss how planning is an iterative process.
In order to save space, the learning objectives of the following chapters are given on another page
II. Optional Chapters
- Interest Rates.
- Risk and Rates of Return.
- Bonds and Their Valuation.
- Stocks and Their Valuation.
- The Cost of Capital.
- The Basics of Capital Budgeting.
- Cash Flow Estimation and Risk Analysis.
- Real Options and Other Topics in Capital Budgeting.
- Capital Structure and Leverage.
- Distributions to Shareholders: Dividends and Share Repurchases.
- Working Capital Management.
- Derivatives and Risks Management
- Multinational Financial Management.
- Hybrid Financing: Preferred Stock, Leasing, Warrants, and Convertibles.
- Mergers and Acquisitions.
Business Finance ePrep Course
– Why Good for You
I. Academic Reasons
This course is an essential foundation for anyone studying accounting, business administration, and other commerce degrees. The concepts taught in this course are fundamental to the business world and will provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the field.
Even students who are not pursuing a business-related degree find this course incredibly beneficial. It is a popular elective that helps students gain knowledge and skills that can be applied to various fields.
Learning new concepts in business finance can be time-consuming and frustrating. However, in this course, a retired professor acts as a personal tutor, providing students with the support they need to succeed. Students can reach out to their tutor via email for personalized consultations.
The course provides clear and detailed explanations of business finance concepts through the course site and the provided textbook. Additionally, students have access to answers and solutions to questions and problems. If they face any difficulty, their tutor is always available for consultations.
Excel spreadsheet software is an essential tool for data analysis and management. Students will learn how to use this software in the course, which will be a valuable skill to have in their future careers.
II. Non-Academic Reasons
- This course not only provides essential principles of business financial management, but also practical knowledge that can be applied to personal finance. You’ll learn skills that can help you make sound financial decisions throughout your life, from budgeting to investing.
- Real-life Singapore Stock fundamental analysis examples are used in this course, which will give you a better understanding of how the stock market works and how to make informed investment decisions. These skills are highly valuable in today’s economy, where knowledge of finance and investment is increasingly in demand.
- Successfully completing this university-level business finance course will set you apart from your peers and impress potential employers with your knowledge and determination. It demonstrates that you take a proactive approach to learning and have the skills and knowledge to make informed financial decisions, both for yourself and for the organizations you work for.
III. For Those Not Going to Universities
If you were unable to pursue university studies due to poor results or only having O or N levels, don’t lose hope. Taking this course seriously could be the inspiration you need to pursue higher education. With the valuable knowledge and skills gained from this business finance course, you will have a better chance of being accepted into a university and succeeding in your academic endeavors. This course is an opportunity to prove to yourself and to others that your potential is not limited by your past academic performance.
Business Finance ePrep Course
– What You Get
I. Free Textbook
“Essentials of Financial Management” which is based on the popular textbook by Eugene F Brigham and Joel F Houston, with chapters adopted by JM Hsu, YK Kong, and AN Bany-Ariffin, 4th Ed. Dr. YK Kong is a professor in NTU NBS, and this business financial management textbook is used in NTU NBS (Examples: AB1201 Financial Management, BU8201 Business Finance, and MiniMasters Finance Fundamentals).
II. Free Consultation
A retired NTU professor is acting as the tutor. You can consult him via email.
III. Materials Online
1 Notes, lecture videos, and PowerPoint files.
2 Answers/solutions to all questions/problems in the textbook.
3 Online exercises.
4 Exercises in using Excel.
5 Real examples of Fundamental analysis of stocks listed in SGX.
6 Bonus learning materials on economics (university level).
IV. Digital Certificate
A digital certificate on business finance will be issued if you complete the ePrep course by passing all the tests at the end of each of the six compulsory chapters.
Business Finance ePrep Course
– Sample Materials
1. Excel Worked Solution (Key Ratios)
Finding Financial Key Ratios from Financial Report
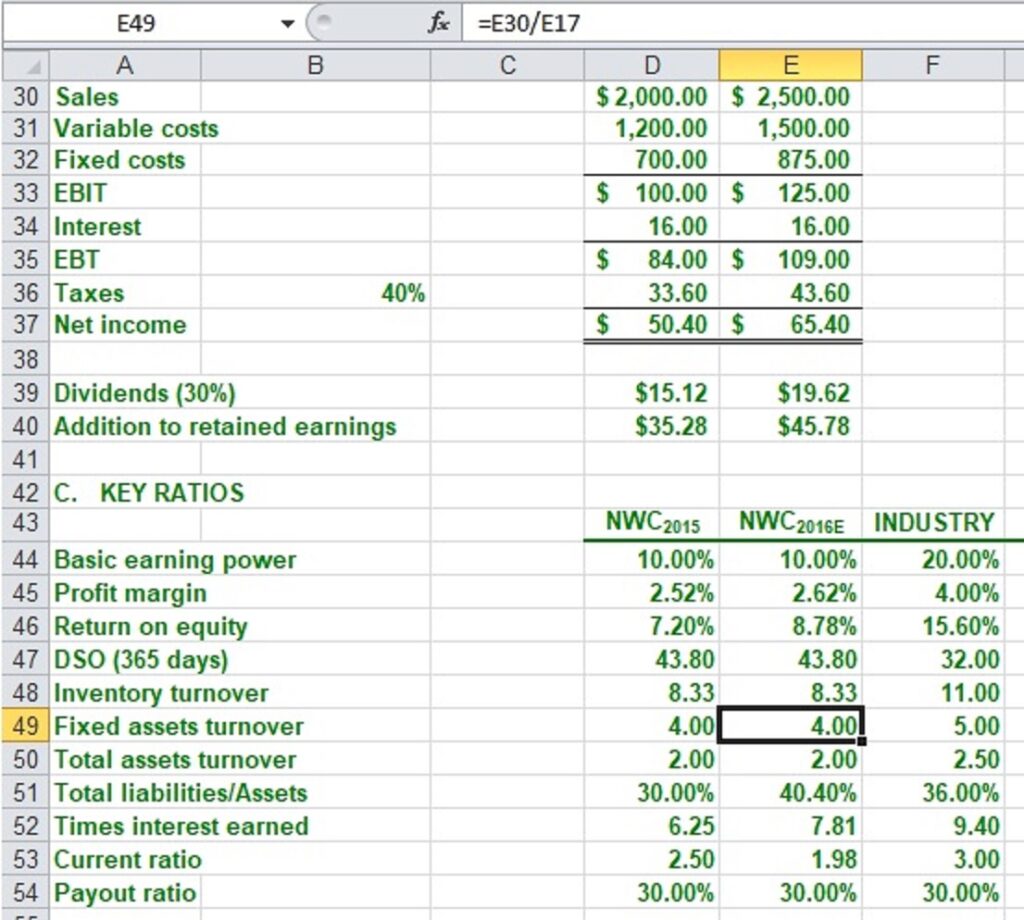
Excel is a very important tool in finance. Using Excel to perform ratio analysis in this exercise serves two important roles: to learn to perform financial ratio analysis and to practice using Excel. Highlighted here is that the “Fixed Asset Turnover” (E49) ratio is given by sales (E30) over total assets (E17, not shown here).
2. Video Lesson (DuPont Equation)
DuPont Equation
This video not only illustrates the principle of the famous DuPont Equation, but it also shows the pitfall of blindly using the return-on-equity ratio as an investment criterion.
3. Problem Walk Through on Video (Economic Value Added)
Finding Economic Value Add – Problem Walk Through
This video problem walkthrough illustrates how to calculate economic value added. It applies the standard equation for computing the economic value-added, and then shows how the values of the different components are computed.
4. Lecture Video Clip (Profitability Ratios)
Profitability Ratios – Examples of Their Determination
This short video clip of a lecture shows how the three profitability ratios are determined.
5. Online Exercise – Response Feebback Providing Rationale (Free Cash Flow)

This exercise example is about the derivation of free cash flow given the financial data of two consecutive years. After submitting the answer, feedback will be provided. As shown in this example, the derivation steps are shown (discarding net incomes as irrelevant information).
6. Question and Answer (Analysis of Financial Statements)
Question:
Why is it sometimes misleading to compare a company’s financial ratios with those of other firms that operate in the same industry?
Answer:
Firms within the same industry may employ different accounting techniques that make it difficult to compare financial ratios. More fundamentally, comparisons may be misleading if firms in the same industry differ in their other investments. For example, comparing PepsiCo and Coca-Cola may be misleading because apart from their soft drink business, Pepsi also owns other businesses, such as Frito‑Lay and Quaker.
Business Finance ePrep Course
Bonus Materials on Economics
Economics (How Changes in Income Affect the Consumer’s Choices)
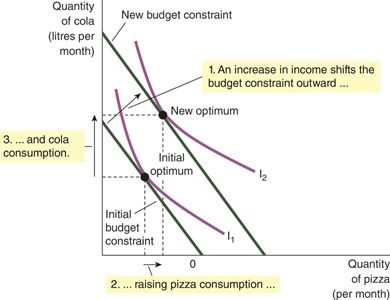
1. A change in income shifts the budget constraints
- An increase in income can be shown by an outward shift of the budget constraint; a decrease in income means that the budget constraint shifts inwards
- Because the relative price of the two goods has not changed, the slope of the budget constraint remains the same
2. An increase in income means that the consumer can now reach a higher indifference curve
3. Because the consumer increased his consumption of both goods when his income increased, both cola and pizza must be normal goods
- Definition of normal good: a good for which an increase in income raises the quantity demanded.
- Definition of inferior good: a good for which an increase in income reduces the quantity demanded
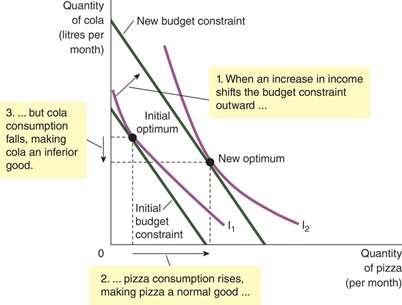
4. In the figure below, cola is an inferior good. The consumer’s income increases yet he buys less cola.
Who should take this Business Finance ePrep Course?
Are you interested in acquiring a strong foundation in business financial management that will prove invaluable in your future academic and professional pursuits? Look no further than our ePrep course in Business Finance, which is a must-do for any student pursuing degrees in accounting, business, and other commerce-related fields. But don’t think this course is only for business students – it is also incredibly useful for any student who may take a course on business finance in their undergraduate programs, or anyone who wants to understand the principles of financial management for personal or work-related investment purposes.
Moreover, this course offers a unique opportunity for individuals who may not be able to proceed to university due to poor results or with only O or N levels to prove that they are capable of completing a university-level business finance course. Best of all, there are no prerequisites to enroll in this course, making it accessible to anyone who wants to learn. And with the popularity of this ePrep course, you can rest assured that you will be joining a community of motivated learners from all walks of life. Don’t miss out on this opportunity – enroll in our Business Finance ePrep course today.
How to Sign Up
1 If You Are an NSF or NSman
SkillsFuture@NS Scheme
You will soon be able to sign up the course using the SF@NS LXP account. Note that there is no upper limit to the number of courses you can sign up for. However, your SF@NS LXP account is valid for only two years.